“Africa heading for a continental breakup.”
The phrase has become increasingly common among analysts, economists, and geopolitical observers. Africa is under intense pressure — climate shocks, separatist conflicts, widening economic inequality, debt crises, and growing foreign influence.
But here’s what many U.S. readers don’t realize: Africa’s stability directly impacts American security, economics, supply chains, and global competitiveness.
Below is an in-depth look at why fragmentation risks are rising — and why the U.S. should be paying close attention.
Why Experts Warn of a Fragmentation Trend
1. Worsening Economic Divergence
According to the World Bank’s analysis of Africa’s economy, some regions (like East Africa) are experiencing rapid digital growth while others (especially parts of West and Central Africa) are stagnating or slipping deeper into debt.
See: World Bank Africa Overview
This uneven development fuels resentment, political instability, and separatist sentiment.

2. Governance Crises and Identity-Based Conflicts
Weak institutions, corruption, and unresolved ethnic disputes continue to destabilize several countries.
Further insight: Africa’s security challenges
These long-standing divides create fertile ground for fragmentation.
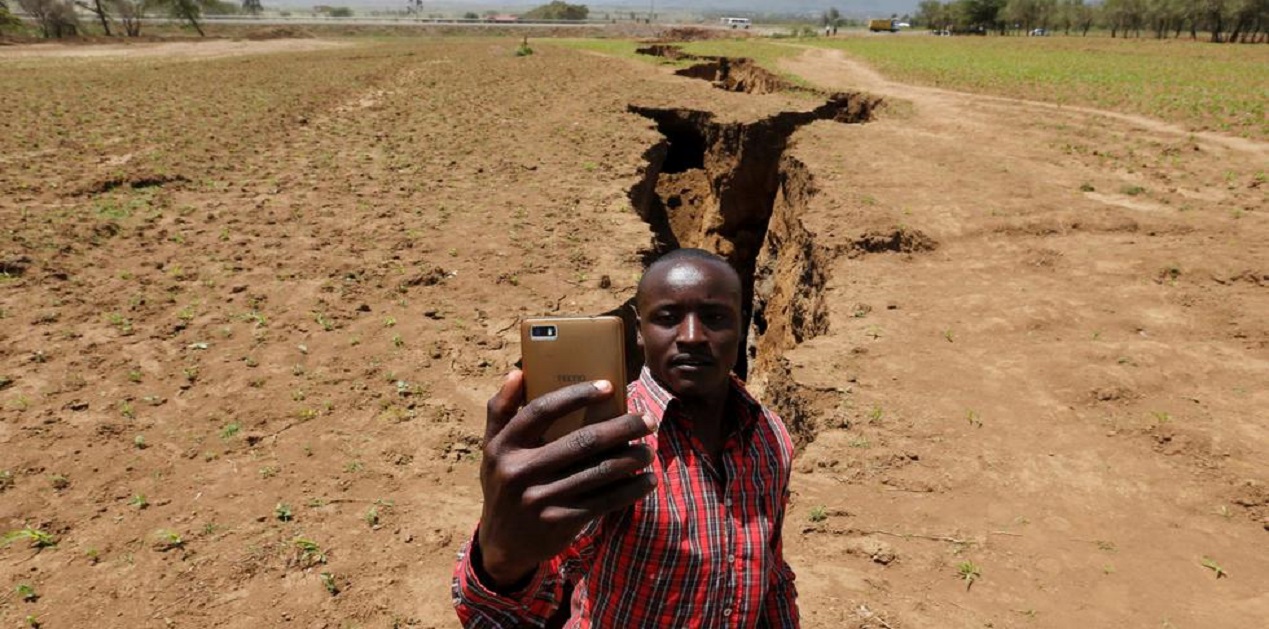
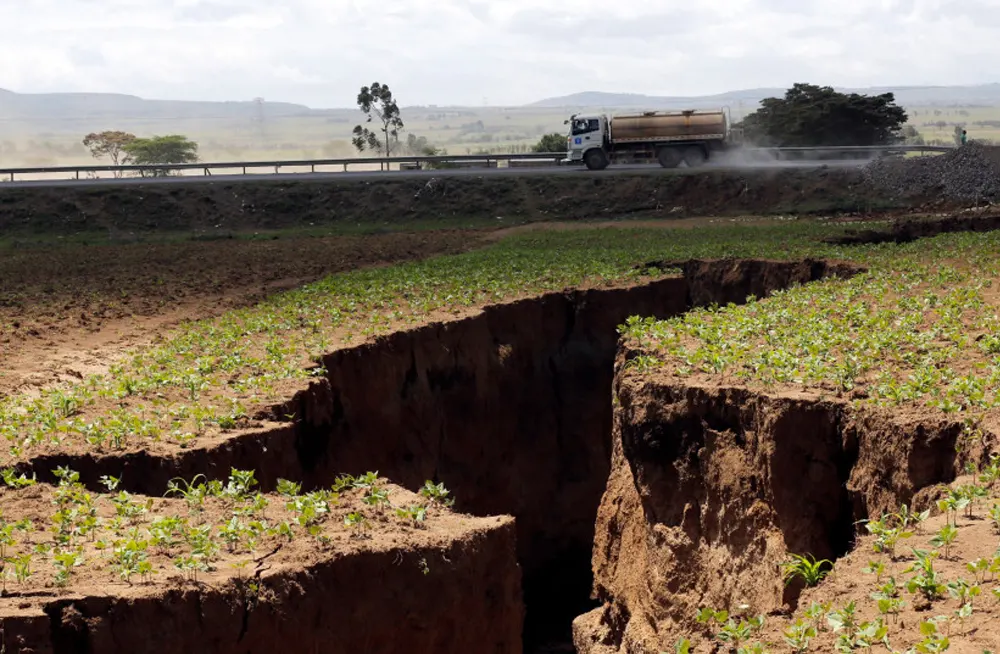
3. Climate Shock Accelerating Instability
Africa is heating faster than most of the world.
See: State of Climate in Africa
Droughts, flooding, and shrinking farmland are pushing communities into conflict and migration.
4. Regional Blocs Moving in Opposite Directions
Africa’s economic zones — ECOWAS, SADC, EAC — increasingly pursue different political agendas.
More details: African Union Regional Economic Communities
This divergence makes a unified African strategy difficult.
5. Rising Foreign Interference
Global powers are deepening influence across the continent.
See: Russia’s growing influence in Africa
Competing alliances often undermine national cohesion.
Where Breakup Pressures Are Most Visible
- Ethiopia: Tigray conflict & Oromo unrest
- Cameroon: Anglophone separatism
- Somalia: Ongoing federal fragmentation
- DRC: Secessionist groups and mineral-region conflict
- Sahel: Coups and extremist expansion in Mali, Niger, Burkina Faso
Real-time conflict data: ACLED conflict tracker
At the same time, cities like Lagos, Nairobi, and Johannesburg continue booming — widening economic divides between rural and urban populations.
Why This Matters Significantly to the United States
1. Critical Minerals for U.S. Tech & Defense Come from Africa
EV batteries, AI servers, solar panels, aircraft systems, and semiconductor components rely on African cobalt, lithium, nickel, and rare earths.
See: White House Supply Chain Report
Fragmentation could disrupt supply chains and raise U.S. manufacturing costs.
2. Terrorism Threats Grow in Fragmented States
Groups like ISIS-Sahel, Al-Shabaab, and Boko Haram thrive in weak states.
Reference: U.S. Department of Defense Releases
Instability increases risks to U.S. interests, embassies, and global security.
3. Rising African Migration to the U.S.
Climate collapse and conflict are pushing Africans into new migration routes toward the southern U.S. border.
More info: Migration Policy Institute
4. U.S.–Africa Trade Disruptions
The lapse of AGOA has already hurt African exporters.
See: Impact on African Exports
Trade instability affects U.S. importers, buyers, and manufacturers.
5. China & Russia Are Expanding Influence
Competitors are filling gaps left by the U.S.
Coverage: Reuters Africa
This shifts global power balances in ways that affect U.S. global strategy.
Trending U.S. News Affecting Africa Policy Bandwidth
1. U.S. Markets Dominated by AI, Fed Rates & Tech
Domestic economic narratives overshadow foreign policy.
See: Reuters U.S. Markets
2. U.S. Military Shifting Focus Toward Venezuela
Navy deployments toward Latin America reduce resources for Africa.
Article: U.S. carrier movement

3. High-Profile Domestic Events Take Priority
Major crises such as mass shootings consume media bandwidth.
Source: AP News
How Africa — And the U.S. — Can Prevent a Breakup
1. Strengthen the African Union
Support continental peacekeeping and negotiation processes.
See: African Union
2. Reduce Corruption & Improve Governance
Promote institutional reforms and transparency.
Reference: Transparency International Africa
3. Invest in Climate Adaptation
Water, agriculture, and coastline protection programs are critical.
Learn more: World Bank Climate Actions
4. U.S. Security Support Without Overreach
Focus on intelligence, training, and local partnership.
See: U.S. AFRICOM
5. Build a Stable U.S.–Africa Trade Strategy
Modernize post-AGOA trade and supply chains.
Analysis: Rethinking AGOA
Africa’s fragmentation is not guaranteed — but the risk is real.
And for the United States, the implications are enormous:
- Critical minerals
- Supply chains
- National security
- Migration
- Geopolitical competition
- Energy and tech development
Africa’s stability is directly tied to America’s economic future and global standing.
#Africa #USPolicy #Geopolitics #GlobalSecurity #AfricaNews #ClimateCrisis #AfricaEconomy #InternationalRelations #GlobalTrends #ContinentalBreakup


