Introduction: Why Small Businesses Are Prime Targets
Cybercriminal no longer focus only on large enterprises. According to data breach investigations, small businesses are increasingly targeted because they often lack mature security defenses.
This is where Zero Trust security comes in—a modern approach designed for today’s cloud-based, remote-first business environment.
What Is Zero Trust (In Plain English)?
Zero Trust is a cybersecurity model based on one simple rule:
Never trust anything. Always verify.
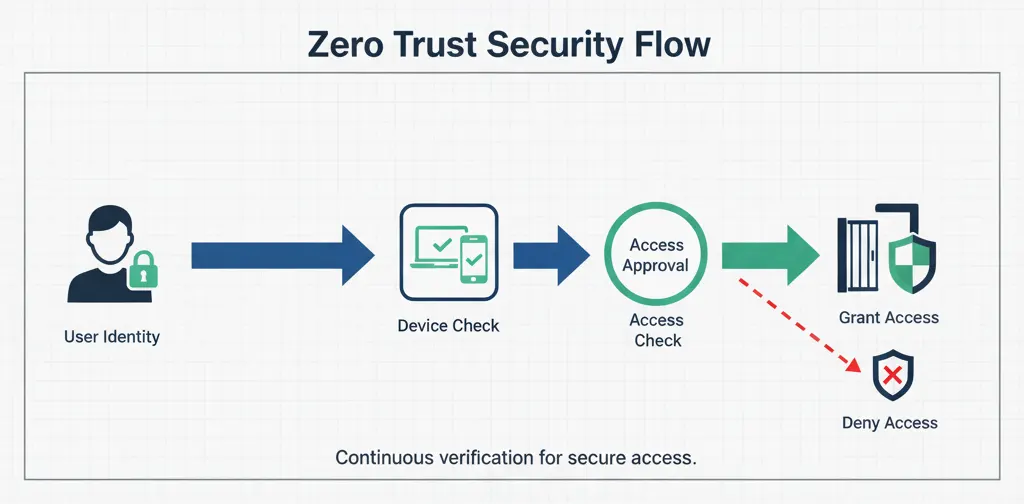
Unlike traditional security models that trust users once they are inside the network, Zero Trust assumes breaches are inevitable and continuously verifies:
- User identity
- Device health
- Location and behavior
- Access permissions
Think of it as airport security—not just one checkpoint, but multiple layers of verification.
Why Traditional Security No Longer Works
Old-school cybersecurity relied on a perimeter—firewalls, VPNs, and internal networks. But modern work has changed. Employees now work from home, cafés, and personal devices.
According to network security research, once attackers breach a traditional perimeter, they can move freely inside systems.
Zero Trust removes that blind trust entirely.
Why Zero Trust Matters for Small Businesses
Small businesses often assume Zero Trust is “enterprise-only.” In reality, it is more critical for smaller teams with limited IT staff.
Guidance from small business cybersecurity programs highlights that most attacks exploit weak passwords, stolen credentials, and unsecured devices—all areas Zero Trust directly addresses.
The Core Pillars of Zero Trust (Simplified)
1. Identity First
Every user must prove who they are—every time. This includes multi-factor authentication (MFA), not just passwords.
2. Device Verification
Zero Trust checks whether a device is secure before granting access. An infected laptop should never access company systems.
3. Least Privilege Access
Users only get access to what they need. This principle, known as least privilege, reduces damage if credentials are compromised.
4. Continuous Monitoring
Suspicious behavior triggers alerts and access restrictions in real time, not after damage is done.
How to Implement Zero Trust on a Small Business Budget
You don’t need a massive IT department to adopt Zero Trust. Many modern SaaS tools already support it.
- Enable MFA across email, cloud apps, and admin accounts
- Use identity providers like Okta or Azure Active Directory
- Apply device policies for company data access
- Segment access between teams and systems

Start small—email and cloud apps are the highest-impact first steps.
Common Zero Trust Myths
“Zero Trust kills productivity.”
In reality, modern tools automate verification in the background, reducing friction.
“We’re too small to be attacked.”
Cybercriminals automate attacks. Size does not equal safety.
“Zero Trust is too complex.”
Cloud-native tools now make Zero Trust easier than traditional security setups.
The Business Benefits Beyond Security
Zero Trust isn’t just about protection—it improves operational resilience. According to industry analysts, Zero Trust reduces downtime, simplifies compliance, and supports remote work at scale.
For small businesses, that translates into:
- Lower breach risk
- Improved customer trust
- Stronger compliance posture
- Future-ready IT infrastructure
Zero Trust Is No Longer Optional
Zero Trust may sound intimidating, but at its core, it’s a mindset shift—not a product purchase.
By assuming breach, verifying continuously, and limiting access, small businesses can achieve enterprise-grade security without enterprise-sized budgets.
In today’s threat landscape, Zero Trust isn’t advanced cybersecurity—it’s basic survival.
#ZeroTrust #CyberSecurity #SmallBusinessSecurity #DataProtection #CloudSecurity #IdentityManagement #InfoSec #BusinessTechnology


